Washington
Washington ranks 31st in industrial emissions. Excluding power plants, refineries and waste are the highest-emitting sectors. Pulp and paper, aircraft manufacturing, and food production are also prominent industries. Industrial activity is concentrated in the western part of the state along the I-5 corridor between Seattle and Portland, Oregon. There are also clusters of industrial development around Spokane and Pasco.
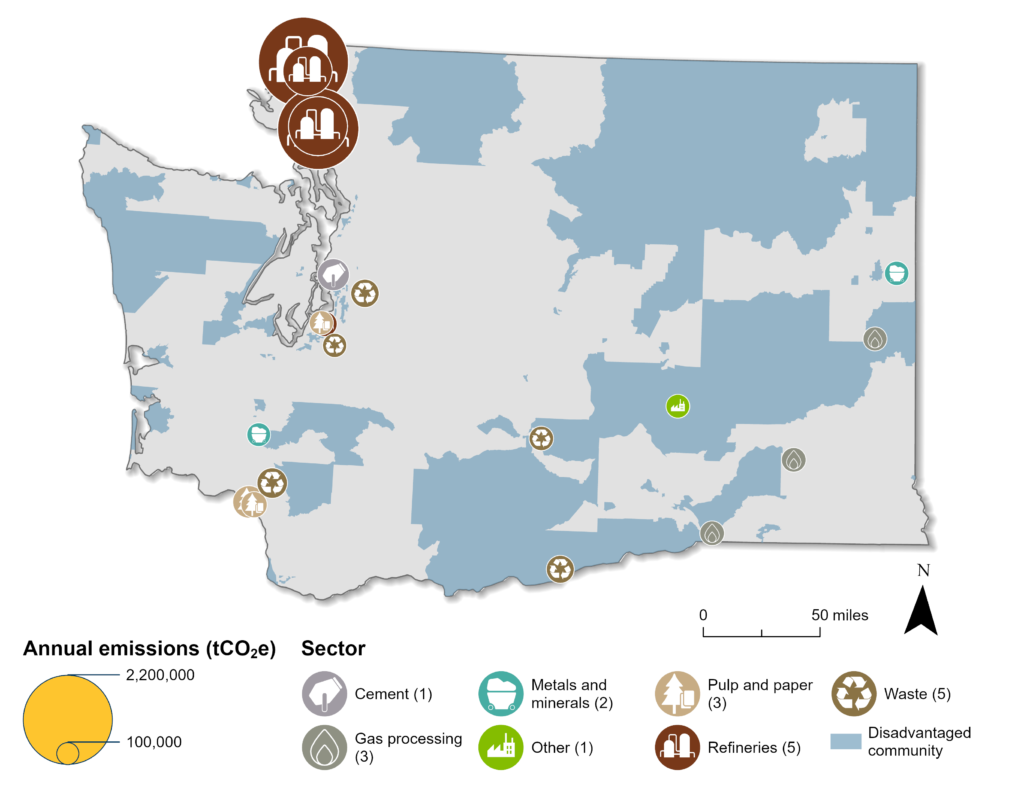
- The top 20 emitters are shown on this map, coded by industrial sector. The size of the circles corresponds to emissions: the larger the circle, the higher the emissions.
- Disadvantaged communities (as determined by the federal government) are shaded blue.
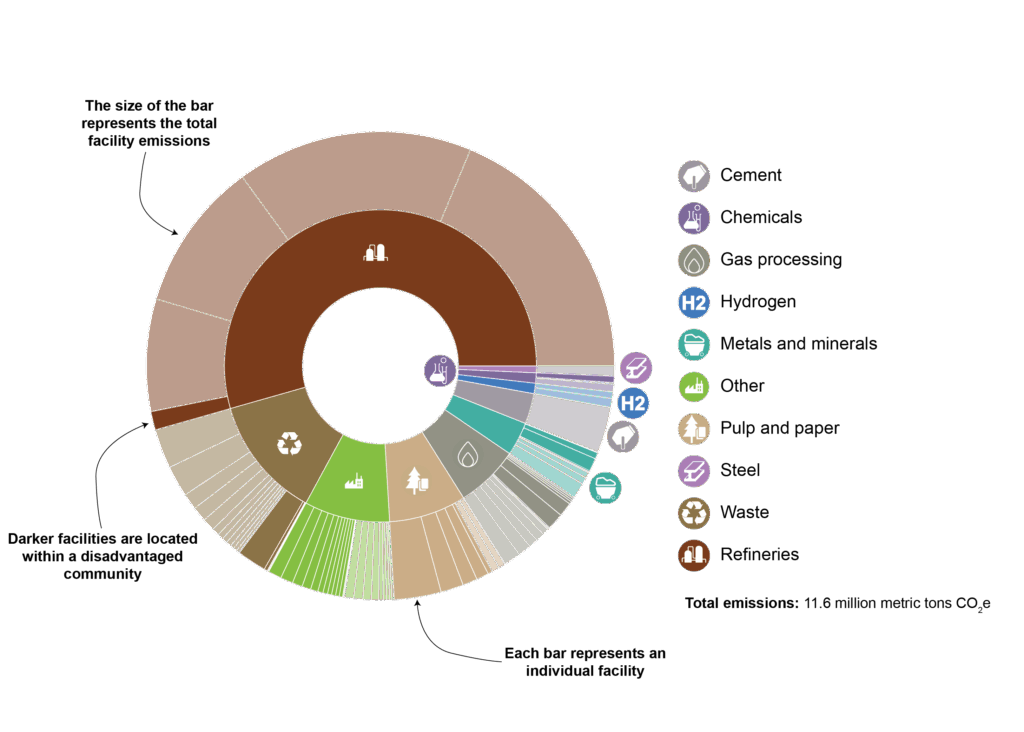
- The inner circle provides a visual representation of the share of emissions generated by each industrial sector.
- The outer circle also indicates the share of a sector’s emissions generated in disadvantaged communities.
STATE ENERGY POLICY:
Considering a state’s broader energy policy landscape is helpful when developing policies to support industrial modernization. Washington has established statutory greenhouse gas emissions targets and a clean energy standard. Washington has not established a clean heat standard. While these formal commitments are not prerequisites for innovative industrial policy, they can provide a supportive framework. In addition, streamlining permitting and establishing an efficient, transparent appeals process that engages local communities early while giving clarity and assurances to project developers are key components of effective state energy policy. Discussions around innovative industrial policy present an opportunity for broader conversations about state energy policy to ensure a mutually reinforcing strategy.
LEGISLATIVE context & opportunity:
Let us know if you are aware of additional legislation advancing industrial innovation in Washington that should be featured. The context below is not exhaustive and serves as an example of recent policies and programs and where there may be future opportunities:
- Buy Clean Buy Fair Washington was enacted in 2024, requiring state agencies and higher education institutions to report on the environmental impacts of certain materials purchased to construct and renovate large, state-owned buildings.
- A factsheet by the Renewable Thermal Collaborative identifies electrification of Washington’s ammonia, pulp and paper, and container glass subsectors as opportunities to reduce emissions significantly.
- Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Association (PNWH2): Washington, Oregon, and Montana are part of the Pacific Northwest Hydrogen Hub. Independent of the outcome of the regional hubs, there is strong interest in building a clean hydrogen economy in the region.
Explore recent legislation in Washington and all 50 states by clicking on a specific year: 2025 legislation, 2024 legislation, 2023 legislation.
