Mississippi
Mississippi ranks 19th in the nation in industrial emissions. Refineries, chemicals, and petroleum and natural gas systems are the highest emitting sectors. Mississippi is also a large pulp and paper producer, accounting for nearly 3 percent of national emissions from the sector. The Columbus, Greenwood, Hattiesburg, and Jackson areas are the primary centers of industrial production.
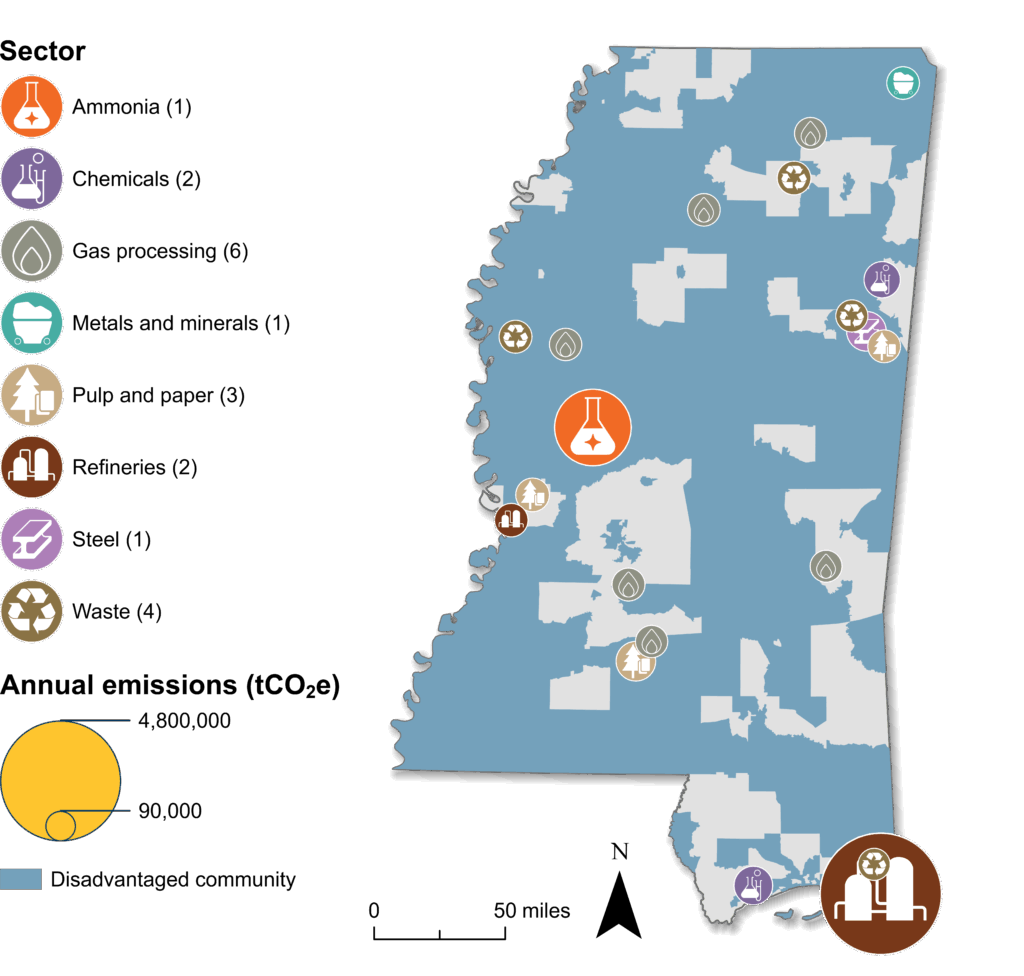
- The top 20 emitters are shown on this map, coded by industrial sector. The size of the circles corresponds to emissions: the larger the circle, the higher the emissions.
- Disadvantaged communities (as determined by the federal government) are shaded blue.
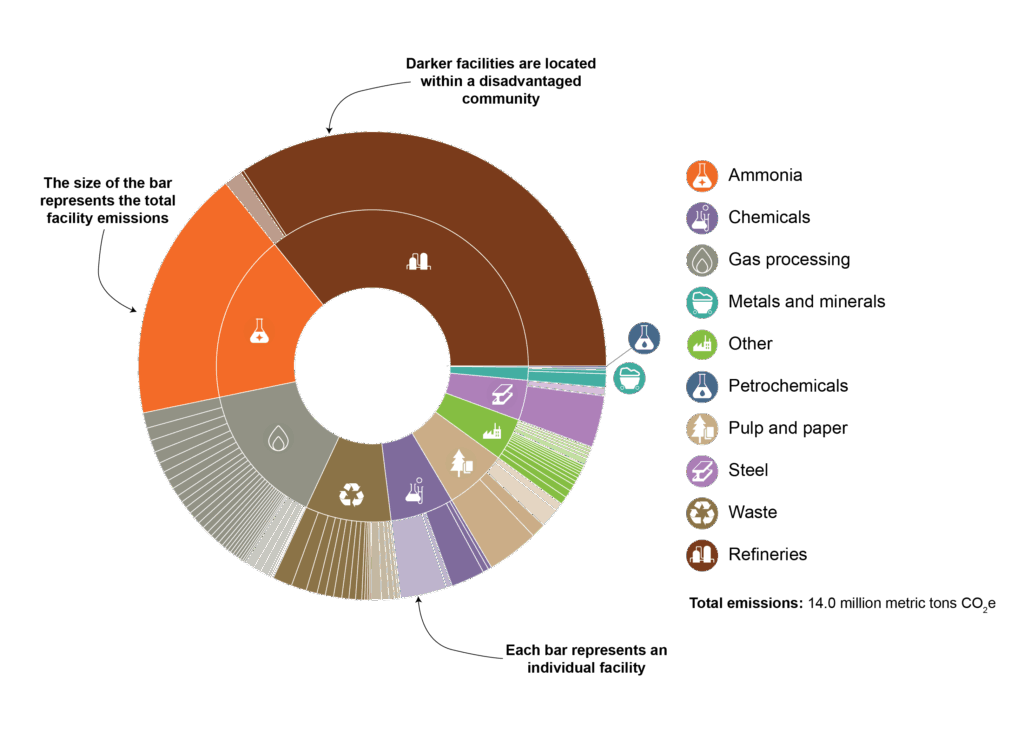
- The inner circle provides a visual representation of the share of emissions generated by each industrial sector.
- The outer circle also indicates the share of a sector’s emissions generated in disadvantaged communities.
STATE ENERGY POLICY:
Considering a state’s broader energy policy landscape is helpful when developing policies to support industrial innovation. Mississippi has not established greenhouse gas emissions targets, an electricity portfolio standard, or a clean heat standard. While these formal commitments are not prerequisites for innovative industrial policy, they can provide a supportive framework. In addition, the development of effective state energy policy requires several key components: streamlining permitting and establishing an efficient, transparent appeals process that engages local communities early while giving clarity and assurances to project developers. Discussions around innovative industrial policy present an opportunity for broader conversations about state energy policy to ensure a mutually reinforcing strategy.
STATE LEGISLATIVE context & opportunity:
Let us know if you are aware of additional legislation advancing industrial innovation in Mississippi that should be featured. The context below is not exhaustive and serves as an example of recent policies and programs, and where there may be future opportunities:
- Senate Concurrent Resolution 569 and House Concurrent Resolution 48 were enacted in 2023, expressing support for the Mississippi Clean Hydrogen Hub and urging the federal government to select Mississippi’s application. The resolutions emphasize Mississippi’s unique geographic and geological characteristics, making it a competitive location for clean hydrogen production. The resolutions also emphasize the potential benefits, including new jobs, economic growth, and positioning Mississippi as a clean hydrogen leader. Independent of the outcome of the regional hubs, there is strong interest in building a clean hydrogen economy in Mississippi.
- The University of Mississippi was selected to receive nearly $750,000 in 2024 to advance clean construction materials, focusing on warm mix asphalt technologies that integrate reclaimed asphalt pavement. The project aims to identify sustainable, durable, and cost-effective asphalt mixtures and collaborate with various stakeholders, including state transportation agencies, to ensure the findings and innovations can be widely adopted and implemented. Independent of the outcome of this grant, there is an opportunity to research and develop advanced construction materials in Mississippi.
Mississippi has enacted and considered a range of legislation that supports industrial innovation, specifically related to carbon management and clean hydrogen. Explore recent legislation in Mississippi and all 50 states by clicking on a specific year: 2025 legislation, 2024 legislation, 2023 legislation.
