Iowa
Iowa ranks 10th in the nation in industrial emissions. Its industrial profile reflects the state’s agriculture-reliant economy. Agricultural processing (labeled “miscellaneous combustion” by the EPA) accounts for more than half of all industrial emissions. Production of non-fluorinated chemicals, primarily ammonia for fertilizer, is responsible for more than a quarter of emissions. Iowa leads the nation in ethanol and biofuel production. Industrial production is concentrated in eastern and central Iowa.

- This map shows the top 20 emitters, coded by industrial sector. The size of the circles corresponds to emissions: the larger the circle, the higher the emissions.
- Disadvantaged communities (as determined by the federal government) are shaded blue.
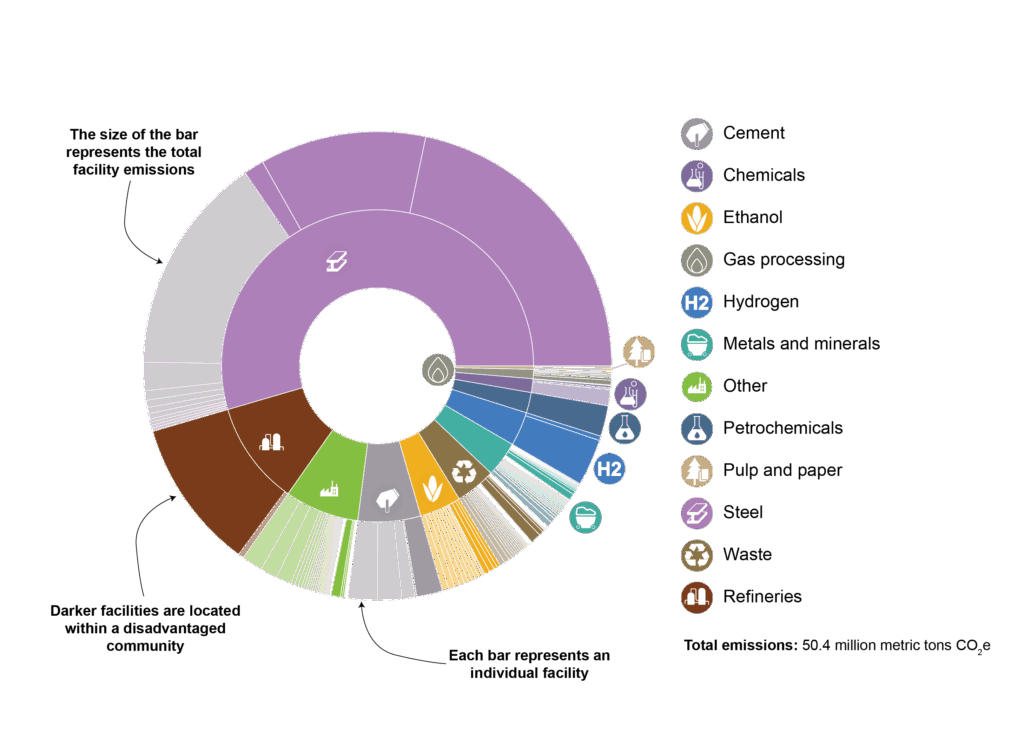
- The inner circle provides a visual representation of the share of emissions generated by each industrial sector.
- The outer circle also indicates the share of a sector’s emissions generated in disadvantaged communities.
STATE ENERGY POLICY:
Examining a state’s broader energy policy landscape is helpful when considering policies to support industrial innovation. Iowa has not established greenhouse gas emissions targets or a clean heat standard. Iowa was the first state to enact a renewable portfolio standard in 1983, but it has since expired. While these formal commitments are not prerequisites for innovative industrial policy, they can provide a supportive framework. In addition, streamlining permitting and establishing an efficient, transparent appeals process that engages local communities early while giving clarity and assurances to project developers are key components of effective state energy policy. Discussions around innovative industrial policy present an opportunity for broader conversations about state energy policy to ensure a mutually reinforcing strategy.
LEGISLATIVE context & opportunity:
Let us know if you are aware of additional legislation advancing industrial innovation in Iowa that should be featured. The context below is not exhaustive and serves as an example of recent policies and programs and where there may be future opportunities:
- Iowa’s deployment of renewables has made it a clean energy leader over the past 20 years (wind and solar generation provided 64 percent of Iowa’s electricity generation in 2023). A 2024 report by the Iowa Environmental Council emphasized that more aggressive action is needed from utilities to reach a carbon-free electricity sector by 2035. Other sectors, like industry, are reliant on these timelines.
- A factsheet by the Renewable Thermal Collaborative identifies electrification of Iowa’s wet corn milling, ammonia, and soybean oil subsectors as opportunities to reduce emissions significantly.
- Carbon management technologies are another opportunity to reduce industrial emissions in the state. Learn more about the economically feasible subsectors in Iowa and facilities that qualify for the federal 45Q tax credit.
Explore recent legislation in Iowa and all 50 states by clicking on a specific year: 2025 legislation, 2024 legislation, 2023 legislation.
